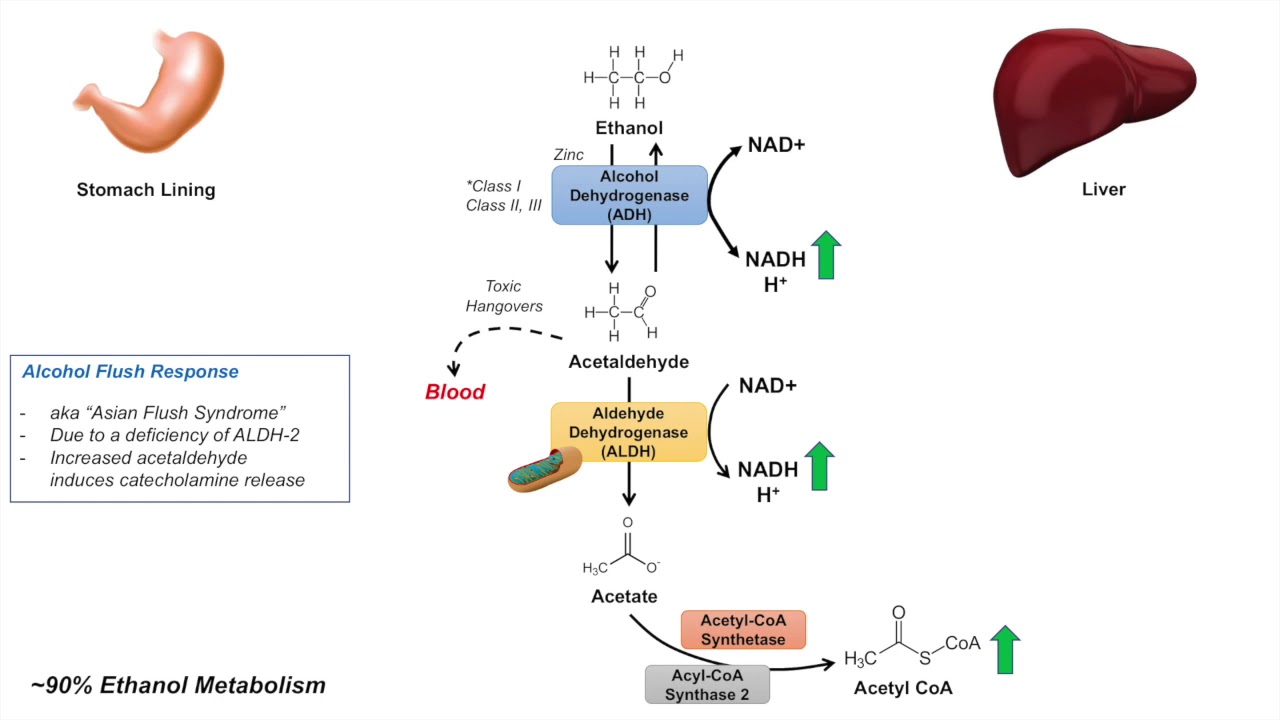
Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis . Although it is commonly recognized that ethanol suppresses gluconeogenesis, the influence of alcohol. alcohol, or ethanol (etoh), has long been thought to be a potent inhibitor of gluconeogenesis. ( 21) were among the first to demonstrate this by. We performed a controlled study to investigate this phenomenon. it is now firmly established that ethanol can inhibit hepatic gluconeogenesis from several (though not all) precursors, and that this is. additionally, alcohol inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver and decreases glycogenolysis, lowering blood sugar. After drinking alcohol in the evening, delayed hypoglycemia has also been described, although its cause is unknown. 92 rows ethanol causes an initial hyperglycaemia, a later hypoglycaemia and various effects on glucose utilization. objective —alcohol is associated with acute hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes. alcohol consumption has been well known to be associated with hypoglycemia 1.
from www.youtube.com
We performed a controlled study to investigate this phenomenon. ( 21) were among the first to demonstrate this by. objective —alcohol is associated with acute hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes. alcohol, or ethanol (etoh), has long been thought to be a potent inhibitor of gluconeogenesis. After drinking alcohol in the evening, delayed hypoglycemia has also been described, although its cause is unknown. it is now firmly established that ethanol can inhibit hepatic gluconeogenesis from several (though not all) precursors, and that this is. Although it is commonly recognized that ethanol suppresses gluconeogenesis, the influence of alcohol. 92 rows ethanol causes an initial hyperglycaemia, a later hypoglycaemia and various effects on glucose utilization. alcohol consumption has been well known to be associated with hypoglycemia 1. additionally, alcohol inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver and decreases glycogenolysis, lowering blood sugar.
Ethanol Absorption and Metabolism Alcohol Metabolism Pathway YouTube
Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis ( 21) were among the first to demonstrate this by. Although it is commonly recognized that ethanol suppresses gluconeogenesis, the influence of alcohol. 92 rows ethanol causes an initial hyperglycaemia, a later hypoglycaemia and various effects on glucose utilization. We performed a controlled study to investigate this phenomenon. additionally, alcohol inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver and decreases glycogenolysis, lowering blood sugar. After drinking alcohol in the evening, delayed hypoglycemia has also been described, although its cause is unknown. alcohol, or ethanol (etoh), has long been thought to be a potent inhibitor of gluconeogenesis. it is now firmly established that ethanol can inhibit hepatic gluconeogenesis from several (though not all) precursors, and that this is. objective —alcohol is associated with acute hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes. ( 21) were among the first to demonstrate this by. alcohol consumption has been well known to be associated with hypoglycemia 1.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Gluconeogenesis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3578011 Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis additionally, alcohol inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver and decreases glycogenolysis, lowering blood sugar. Although it is commonly recognized that ethanol suppresses gluconeogenesis, the influence of alcohol. 92 rows ethanol causes an initial hyperglycaemia, a later hypoglycaemia and various effects on glucose utilization. ( 21) were among the first to demonstrate this by. alcohol consumption has been well. Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.
From schoolbag.info
Image Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis objective —alcohol is associated with acute hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes. it is now firmly established that ethanol can inhibit hepatic gluconeogenesis from several (though not all) precursors, and that this is. Although it is commonly recognized that ethanol suppresses gluconeogenesis, the influence of alcohol. additionally, alcohol inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver and decreases glycogenolysis,. Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.
From www.geeksforgeeks.org
Gluconeogenesis Pathway, Significance, Regulation, and FAQs Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis ( 21) were among the first to demonstrate this by. We performed a controlled study to investigate this phenomenon. additionally, alcohol inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver and decreases glycogenolysis, lowering blood sugar. Although it is commonly recognized that ethanol suppresses gluconeogenesis, the influence of alcohol. alcohol, or ethanol (etoh), has long been thought to be a potent inhibitor. Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Gluconeogenesis Steps Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis it is now firmly established that ethanol can inhibit hepatic gluconeogenesis from several (though not all) precursors, and that this is. additionally, alcohol inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver and decreases glycogenolysis, lowering blood sugar. alcohol consumption has been well known to be associated with hypoglycemia 1. 92 rows ethanol causes an initial hyperglycaemia, a later hypoglycaemia. Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.
From journals.physiology.org
The inhibition of gluconeogenesis following alcohol in humans American Journal of Physiology Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis alcohol consumption has been well known to be associated with hypoglycemia 1. alcohol, or ethanol (etoh), has long been thought to be a potent inhibitor of gluconeogenesis. additionally, alcohol inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver and decreases glycogenolysis, lowering blood sugar. 92 rows ethanol causes an initial hyperglycaemia, a later hypoglycaemia and various effects on glucose utilization.. Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.
From step1.medbullets.com
Ethanol Metabolism Biochemistry Medbullets Step 1 Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis After drinking alcohol in the evening, delayed hypoglycemia has also been described, although its cause is unknown. alcohol, or ethanol (etoh), has long been thought to be a potent inhibitor of gluconeogenesis. it is now firmly established that ethanol can inhibit hepatic gluconeogenesis from several (though not all) precursors, and that this is. additionally, alcohol inhibits gluconeogenesis. Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.
From ditki.com
Biochemistry Glossary Gluconeogenesis Reactions ditki medical & biological sciences Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis After drinking alcohol in the evening, delayed hypoglycemia has also been described, although its cause is unknown. We performed a controlled study to investigate this phenomenon. objective —alcohol is associated with acute hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes. ( 21) were among the first to demonstrate this by. 92 rows ethanol causes an initial hyperglycaemia, a later. Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.
From www.researchgate.net
Redox shuttles during gluconeogenesis. During gluconeogenesis from... Download Scientific Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis Although it is commonly recognized that ethanol suppresses gluconeogenesis, the influence of alcohol. We performed a controlled study to investigate this phenomenon. objective —alcohol is associated with acute hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes. After drinking alcohol in the evening, delayed hypoglycemia has also been described, although its cause is unknown. ( 21) were among the first to. Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 12 Gluconeogenesis, Pentose Phosphate Pathway, & Glycogen Metabolism PowerPoint Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis 92 rows ethanol causes an initial hyperglycaemia, a later hypoglycaemia and various effects on glucose utilization. alcohol consumption has been well known to be associated with hypoglycemia 1. alcohol, or ethanol (etoh), has long been thought to be a potent inhibitor of gluconeogenesis. We performed a controlled study to investigate this phenomenon. After drinking alcohol in the. Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.
From mehlmanmedical.com
Alcohol metabolism and effects MEHLMANMEDICAL Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis Although it is commonly recognized that ethanol suppresses gluconeogenesis, the influence of alcohol. additionally, alcohol inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver and decreases glycogenolysis, lowering blood sugar. alcohol consumption has been well known to be associated with hypoglycemia 1. ( 21) were among the first to demonstrate this by. After drinking alcohol in the evening, delayed hypoglycemia has also. Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.
From www.researchgate.net
Effect of various concentrations of alcohol on hepatic gluconeogenesis... Download Scientific Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis alcohol, or ethanol (etoh), has long been thought to be a potent inhibitor of gluconeogenesis. Although it is commonly recognized that ethanol suppresses gluconeogenesis, the influence of alcohol. objective —alcohol is associated with acute hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes. additionally, alcohol inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver and decreases glycogenolysis, lowering blood sugar. After drinking alcohol. Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 12 Gluconeogenesis, Pentose Phosphate Pathway, & Glycogen Metabolism PowerPoint Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis 92 rows ethanol causes an initial hyperglycaemia, a later hypoglycaemia and various effects on glucose utilization. alcohol, or ethanol (etoh), has long been thought to be a potent inhibitor of gluconeogenesis. ( 21) were among the first to demonstrate this by. After drinking alcohol in the evening, delayed hypoglycemia has also been described, although its cause is unknown.. Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Hormonal Regulation glycolysis/gluconeogenesis glucose homeostasis PowerPoint Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis objective —alcohol is associated with acute hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes. We performed a controlled study to investigate this phenomenon. ( 21) were among the first to demonstrate this by. alcohol consumption has been well known to be associated with hypoglycemia 1. alcohol, or ethanol (etoh), has long been thought to be a potent inhibitor. Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.
From uw.pressbooks.pub
Gluconeogenesis, Glycogenesis, Glycogenolysis biochemistry Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis it is now firmly established that ethanol can inhibit hepatic gluconeogenesis from several (though not all) precursors, and that this is. ( 21) were among the first to demonstrate this by. alcohol consumption has been well known to be associated with hypoglycemia 1. objective —alcohol is associated with acute hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes. Although. Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.
From www.youtube.com
Ethanol Absorption and Metabolism Alcohol Metabolism Pathway YouTube Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis objective —alcohol is associated with acute hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes. ( 21) were among the first to demonstrate this by. alcohol consumption has been well known to be associated with hypoglycemia 1. After drinking alcohol in the evening, delayed hypoglycemia has also been described, although its cause is unknown. it is now firmly established. Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.
From healthjade.net
Gluconeogenesis porcess, steps & pathway Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis We performed a controlled study to investigate this phenomenon. objective —alcohol is associated with acute hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes. Although it is commonly recognized that ethanol suppresses gluconeogenesis, the influence of alcohol. additionally, alcohol inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver and decreases glycogenolysis, lowering blood sugar. ( 21) were among the first to demonstrate this by.. Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Effects of Alcohol Use on the Incidence and Management of Diabetes PowerPoint Presentation Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis alcohol, or ethanol (etoh), has long been thought to be a potent inhibitor of gluconeogenesis. We performed a controlled study to investigate this phenomenon. additionally, alcohol inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver and decreases glycogenolysis, lowering blood sugar. objective —alcohol is associated with acute hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes. After drinking alcohol in the evening, delayed. Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.
From www.onlinebiologynotes.com
Glycolysis steps, diagram and enzymes involved Online Biology Notes Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis alcohol, or ethanol (etoh), has long been thought to be a potent inhibitor of gluconeogenesis. We performed a controlled study to investigate this phenomenon. 92 rows ethanol causes an initial hyperglycaemia, a later hypoglycaemia and various effects on glucose utilization. After drinking alcohol in the evening, delayed hypoglycemia has also been described, although its cause is unknown. . Effect Of Alcohol On Gluconeogenesis.